Explain the Different Types of Body Symmetry in Animals
The butterfly and most mammals are symmetrical along the main body axis. At a very basic level of classification true animals can be largely divided into three groups based on the type of symmetry of their body plan.

Animal Architecture Zoology What Is An Animal An
Cockroaches have a body structure that facilitates walking climbing and flying.

. Symmetry biology A selection of animals showing the range of possible symmetries including both radial and bilateral body plans. Bilateral means two sides The animal can be divided into right and left halves and crayfish are an example. Bilateral mirror symmetry is symmetrical with respect to its reflection.
Coelom is the main body cavity in most of the animals which is located between the intestinal canal and the body. Only a few animal groups display radial symmetry. The animal which looks same on all sides from the centre is referred to as Radial symmetry.
Examples are Coelenterates ctenophores and echinoderms. Key Takeaways Animal Characterization Based on Body Symmetry. They are asymmetrical radial or bilateral in form as illustrated in Figure 6.
Birds have light bones attached to strong muscles which help them to fly. Can bones be asymmetrical. Annelids Arthropods Molluscs etc.
Fish is an aquatic animal adapted to live in water. The two sides are. The three types of symmetry are.
The body plans of most multicellular organisms have some form of symmetry radial symmetry bilateral symmetry or spherical symmetry. The organisms body generates identical sides in any plane which it is divided along the central axis. Animal Body Planes and Cavities.
An example of an asymmetrical animal is a sponge. A coelom is a body cavity. At a very basic level of classification true animals can be largely.
The body cavity of animals which differentiate whether they have a true body cavity or no which is known as Coelom. Whereas hind limb bones are modified to walk and perch. The body of the organism generates two sides as left and right along the sagittal plane.
Body cavity also acts as shock absorber and protects the internal organs. Asymmetrical means it has no symmetry and sponges are an example. Bilateral symmetry involves the division of the animal through a midsagittal plane resulting in two superficially mirror images right and left halves such as those of a butterfly d crab or human bodyAnimals with bilateral symmetry have a head and tail anterior vs.
Learn about body plans the types of body symmetry body cavities and tissues and. Symmetry is a pattern classification scheme. Animals can be classified by three types of body plan symmetry.
The vast majority of animals however exhibit a definite symmetrical form. Their body is covered by a hard outer skeleton. Four such patterns of symmetry occur among animals.
Radial symmetry bilateral symmetry and asymmetry. Tissues and Body cavities. Spherical radial biradial and bilateral.
Identify the different types of BODY SYMMETRIES seen in animals. Radially symmetrical bilaterally symmetrical and asymmetrical. A symmetry where any plane passing through the central axis divides the body into two equal halves is called the radial symmetry.
Some animals have sides looking mirror image of one another such body plan is called Bilateral symmetry. The acoelomates eg flatworms flukes and tapeworms the pseudocoelomates eg roundworms pinworms hookworms and rotifers and the. Bilateral symmetry means that if you cut that organism from the middle you will get two equal halves.
The body plans of animals have different classifications and features that are affected by various factors. Ventral and right and left sides. Start studying the ch.
Asymmetry is a unique feature of Parazoa link a. Radial symmetry as illustrated in Figure 6 describes when an animal has an up-and-down. Identify the 3 types of BODY CAVITIES that are seen in animals.
In bilateral symmetry only a single plane divides the body into two equal halves eg. Evolution of body cavity is an important event which further helped the formation of efficient body systems to support growing organs and distribute material. Posterior front and back dorsal vs.
Radial symmetry is the arrangement of body parts around a central axis like rays on a sun or pieces in. Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. How do they differ from each other and what advantages andor disadvantages does each body cavity possess.
16 biology flashcards containing study terms like Give an example of an animal with bilateral symmetry not mentioned in the text Use the characteristics of animals to show that a Holstein cow Bos primi-genius used for milk production on dairy farms is an animal Rotifers. It is found in organisms with bilateral symmetry. Asymmetrical animals are animals with no pattern or symmetry.
Asymmetrical radial and bilateral. Symmetry in biology is about the overall shape of the body and its parts. Radial means body parts are arranged in a circle around a center point and jellyfish are an example.
Coelomates and Pseudocoelomates Figure 2 illustrates the three basic body plans encountered in the bilateria. Considering this what are the three possible types of body cavities an animal can have. How do they differ from each other and what advantages andor disadvantages does each symmetry possess.
The body is obviously made of layers upon layers of cells and these cells are. Bilateral variations in dimensions of upper and lower limb bones are attributable to difference in mechanical stress and strain that the bones are subjected to during bone growth and is referred to as directional. There are various symmetry classifications including.
Animal body plans follow set patterns related to symmetry.
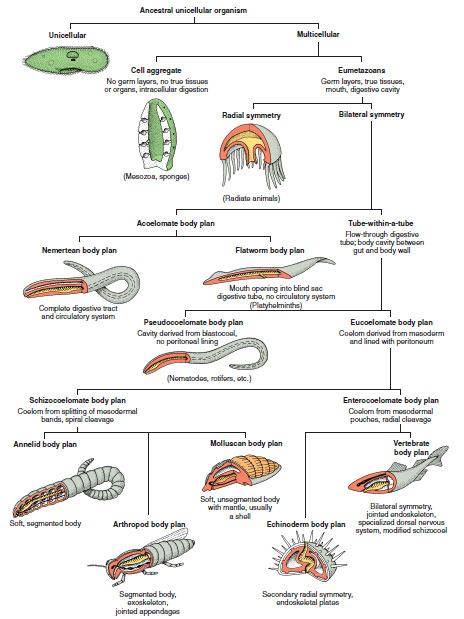
Animal Body Plans Architectural Pattern Of An Animal The Diversity Of Animal Life

What Do You Mean By Radially Symmetercal Body Find 12 Answers Solutions Learnpick Resources
Why Is Radial Symmetry Uncommon For Land Animals Quora

Bilateral Symmetry Definition Examples Advantages Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Learn About Symmetrical Body Plan Chegg Com

Types Of Symmetry And Animal Bodies Symmetry Is The Arrangement Of Body Parts Around A Central Plane Or Axis Asymmetry Occurs When The Body Can T Ppt Download

Features Used To Classify Animals Boundless Biology

Three Different Type Of Symmetry In Organisms From Left To Right Download Scientific Diagram
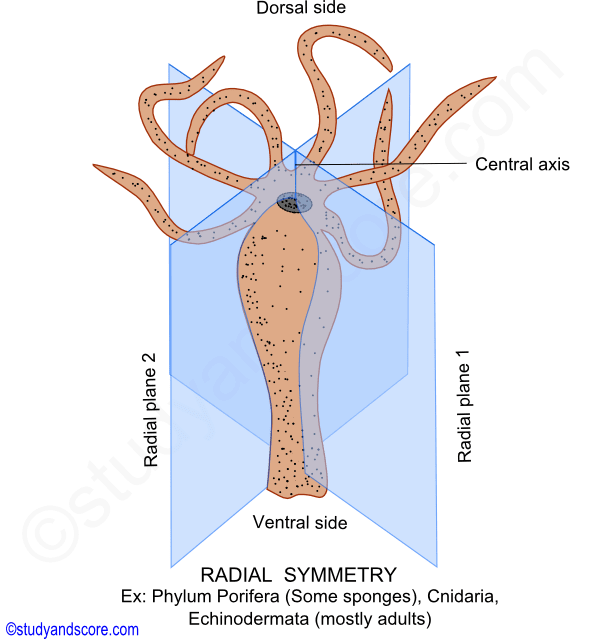
Symmetry In Animals Types Of Symmetry Bilateria And Radiata Study Score

Describe Types Of Symmetry In Animals
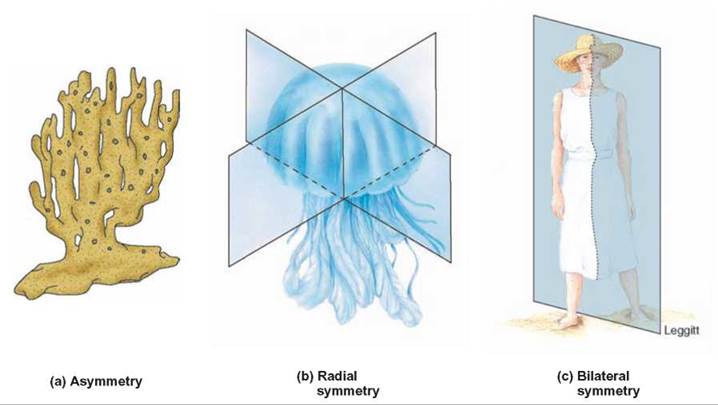
Body Plans The Animal Kingdom The Origin And Classification Of Life Concepts In Biology

Learn About Bilateral Symmetry Of Animals Chegg Com

Bilateral Left Right Symmetry Understanding Evolution

The Major Types Of Body Plans A Asymmetry B Radial Symmetry Download Scientific Diagram

Types Of Symmetry In Animals Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


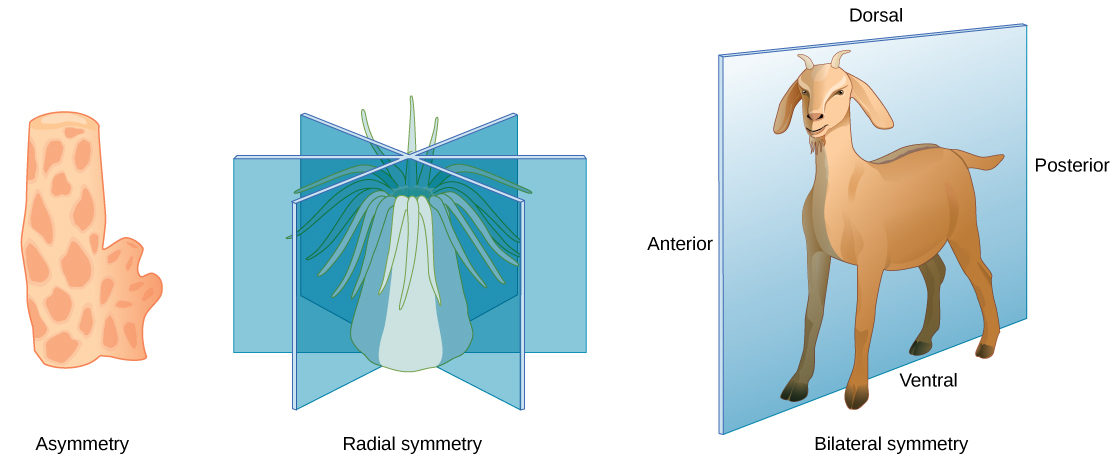
Comments
Post a Comment